AI in customer service: The ultimate guide for 2025
What is AI in customer service?
AI in customer service refers to using artificial intelligence technologies to automate, enhance, or support customer interactions. This can involve chatbots, virtual assistants, and machine learning systems that handle inquiries, resolve issues, or offer personalized recommendations to enhance the user journey. By analyzing customer data and behaviors, AI improves efficiency, reduces response times, and enables businesses to provide more tailored and proactive support.
In this blog, we'll discuss everything you need to know about generative conversational AI in customer service - from trends, technology, and use cases to learning how to make your own AI chatbot. Let's dive in!
Let's start by answering the question, "What is generative conversational AI?"
Note: While AI customer service is the main topic of discussion, please note that there are subtle differences between customer support vs. customer service.
In this blog, 'customer support' and 'customer service' are used interchangeably.
What is generative conversational AI?
Generative conversational AI refers to a type of artificial intelligence system designed to engage in human-like conversations and generate natural language responses, as opposed to a rule-based chatbot. These AI systems use techniques like Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning to understand and generate conversational text-based or spoken responses.
Let’s break this down into its constituent parts - conversational AI and generative AI.
What is conversational AI?
Conversational AI is an umbrella term that encompasses all the AI technologies that enable computers to simulate human conversations. For example, conversational AI includes chat, voice search, and voice-activated smart devices.
What is generative AI?
According to McKinsey, “Generative artificial intelligence (AI) describes algorithms (such as ChatGPT) that can be used to create new content, including audio, code, images, text, simulations, and videos.”
A generative AI model will create new content that closely resembles examples similar to the data it has ingested. Generative AI models take raw data - which can be anything from a technical user manual to a description of artwork - and create a statistically probable output. Generative AI models are trained on massive datasets; the larger the dataset, the more information the model has to work with while being trained.
Customer support chat is an area in which generative conversational AI is extremely useful. Within the customer support chat use case, there is both a need for cutting-edge conversational AI from a customer perspective and the potential to make a significant impact from the business perspective. For example:
62% of people would rather use a chatbot than call customer support
AI chatbots can reduce customer support costs by 30%
According to Juniper Research, 90% of companies that used chatbots for customer support saw a mere 70¢ cost per interaction and saved 4 minutes per customer support request
Businesses can achieve this with Sendbird’s conversational AI solution. This solution for customer support allows customer service agents to:
Reduce time to ticket resolution by 30%
Increase agent productivity by 30% - 50%
Increase CSAT by 2%
How can your business achieve these results? We’ll take a look at Sendbird’s conversational AI solution in action, understand how to build and deploy an AI chatbot for customer support, and learn more about the impact businesses can achieve with AI in customer service.

Build & deploy your own custom AI chatbot in minutes for free
How conversational AI has unveiled a new reality for AI in customer service
From the rule-based chatbots of the 2010s to the modern generative AI that powers ChatGPT, AI chatbots have come a long way. ChatGPT’s meteoric rise of 1 million users in 5 days (a record broken only by Threads) and worldwide adoption, along with the various ChatGPT integrations mushrooming all over, indicate that AI chatbots may become an integral part of our lives.
From the perspective of businesses, AI chatbots help with:
Generating leads by proactively asking questions and storing information
Collecting user feedback while the site experience is still fresh
Notifying users about ongoing promotions, sales, and discounts
Offering product recommendations based on previous purchases
Delivering order updates and sending alerts
Ticket deflection through robust self-service options such as an FAQ bot
For users, AI chatbots are a great tool for:
Getting quick answers in a time crunch
Receiving detailed explanations without needing to search
Checking a bank balance, paying a bill, or applying for a loan
Making a reservation or appointment
Scheduling a meeting
Buying an item
Requesting a refund or exchange
Booking tickets
While all of these chatbot use cases are important and useful, one of the most important applications of AI chatbots is in customer support. Let’s take a deeper look at conversational AI in customer service.

Build & deploy your own custom AI chatbot in minutes for free
Why conversational AI in customer service? A closer look at the numbers
Conversational AI is revolutionizing customer support. With the conversational AI market set to grow to nearly $30 billion by 2028, the market is set on a strong path of growth. Specifically, the chatbot market is expected to be worth $24.64 billion by 2030. Revenue forecasts remain strong: the chatbot market is expected to receive nearly $455 million in revenue by 2027.
While the dollar numbers are encouraging, user interest in chatbots overall is rising, likely spurred by the release and worldwide popularity of ChatGPT. Indeed, searches for the term ‘ai chatbot’, which had been seeing only a slight increase, exploded after the release of ChatGPT.
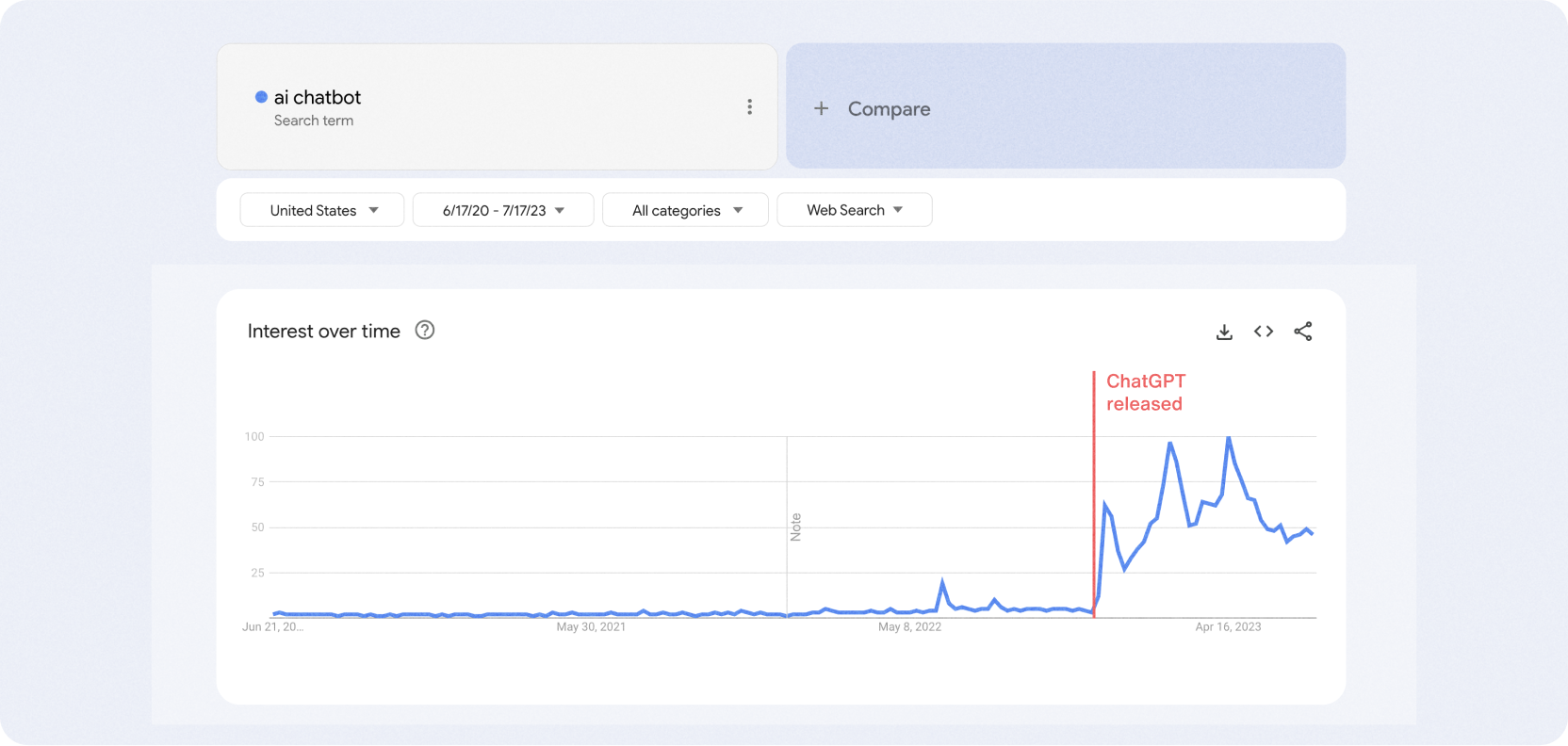
It’s clear that money and user interest both exist - but do these make an impact in the world of AI in customer service? What did companies that invested in chatbots find?
What are the real benefits of conversational AI in customer service?
Let’s answer this question from two perspectives: that of the customer and that of the business.
The customer’s perspective on conversational AI in customer service
We have all experienced the frustrations of reaching out to customer service representatives. From being put on hold to repeating the same information multiple times and finally ending the conversation with our query unresolved, we are not strangers to the challenges of talking to customer support.
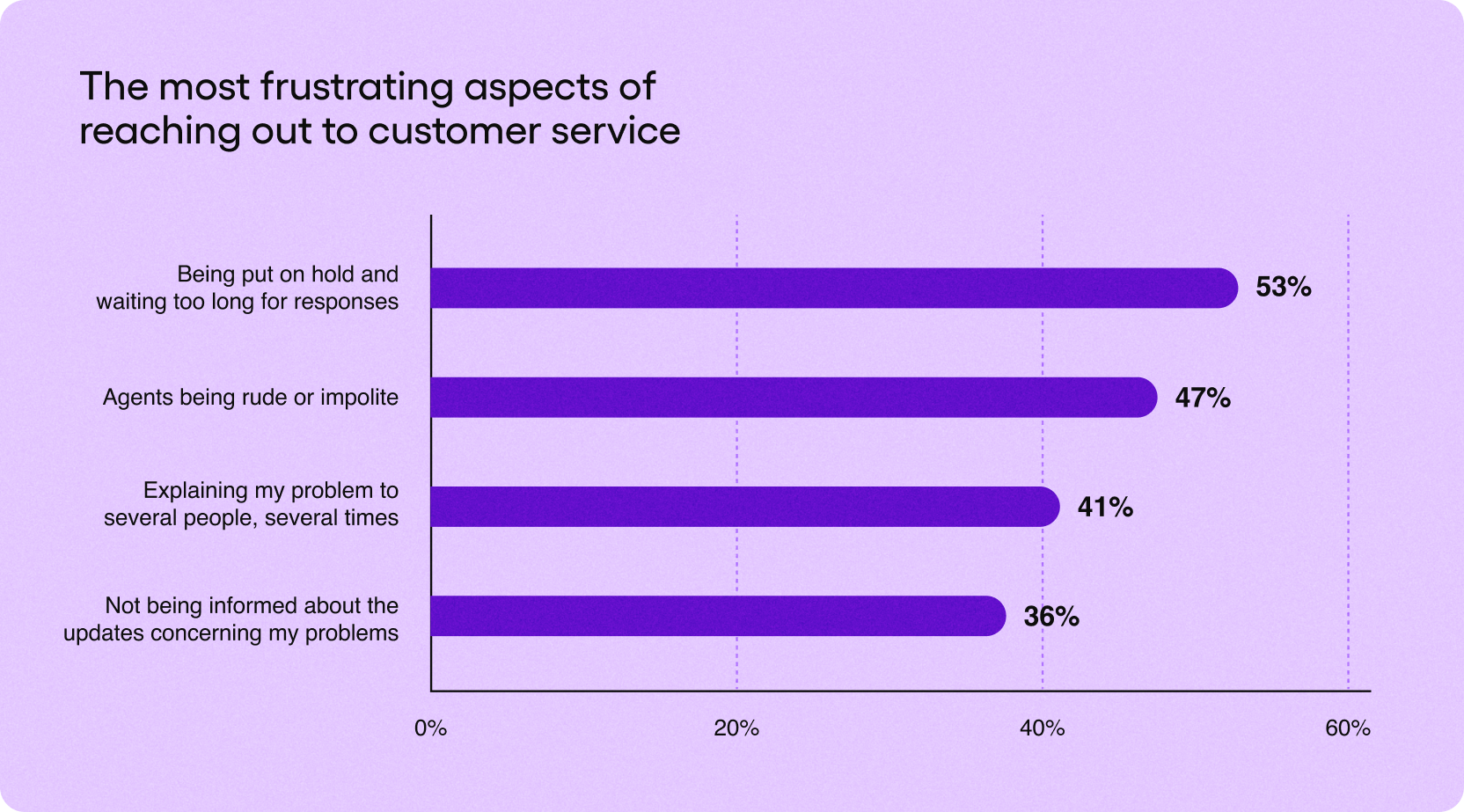
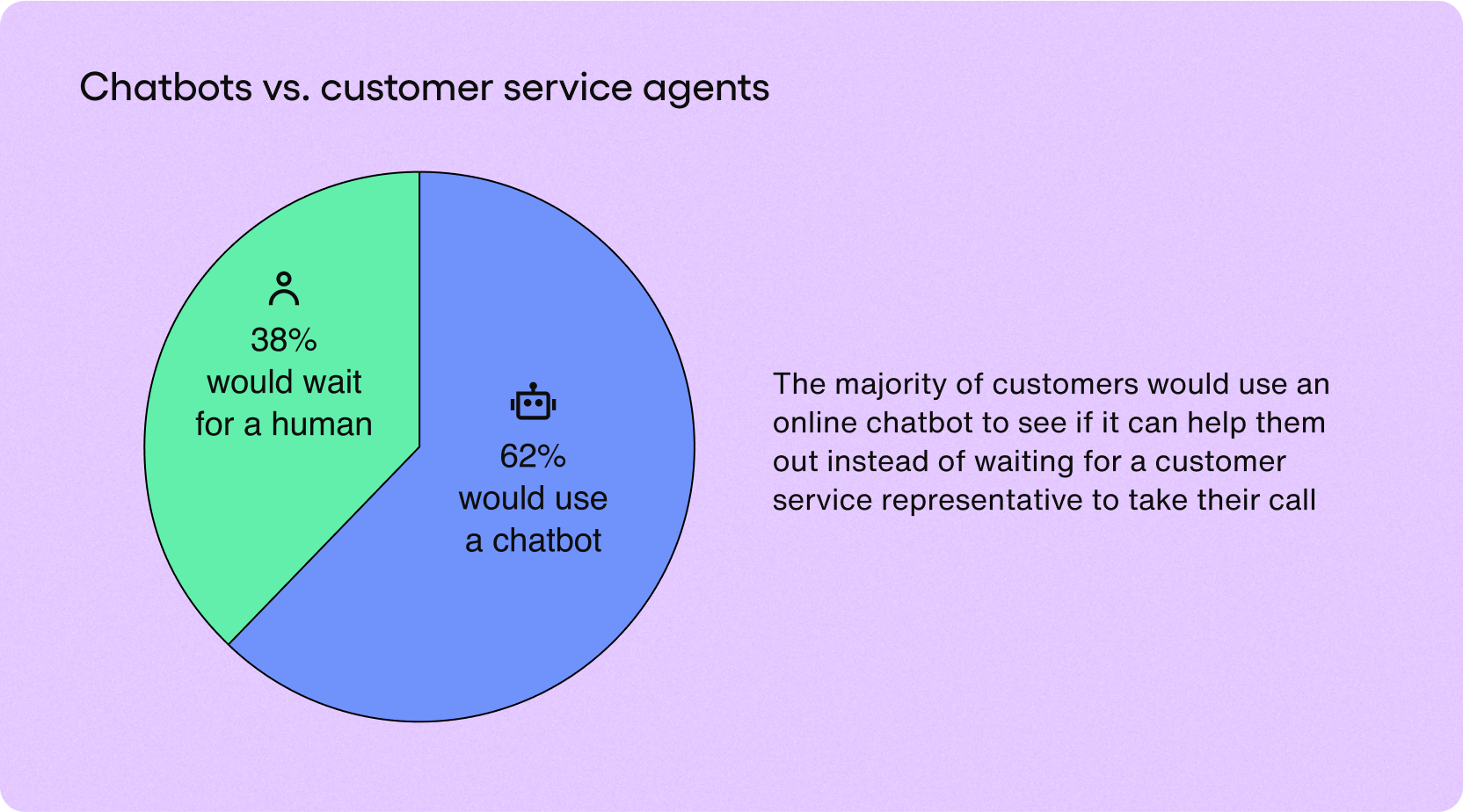
Indeed, the majority of people would prefer to speak to a chatbot instead of talking to a human customer service representative!
In a global consumer channel preferences study, it was found that Millennials and Gen Z were the most likely to prefer talking to chatbots.
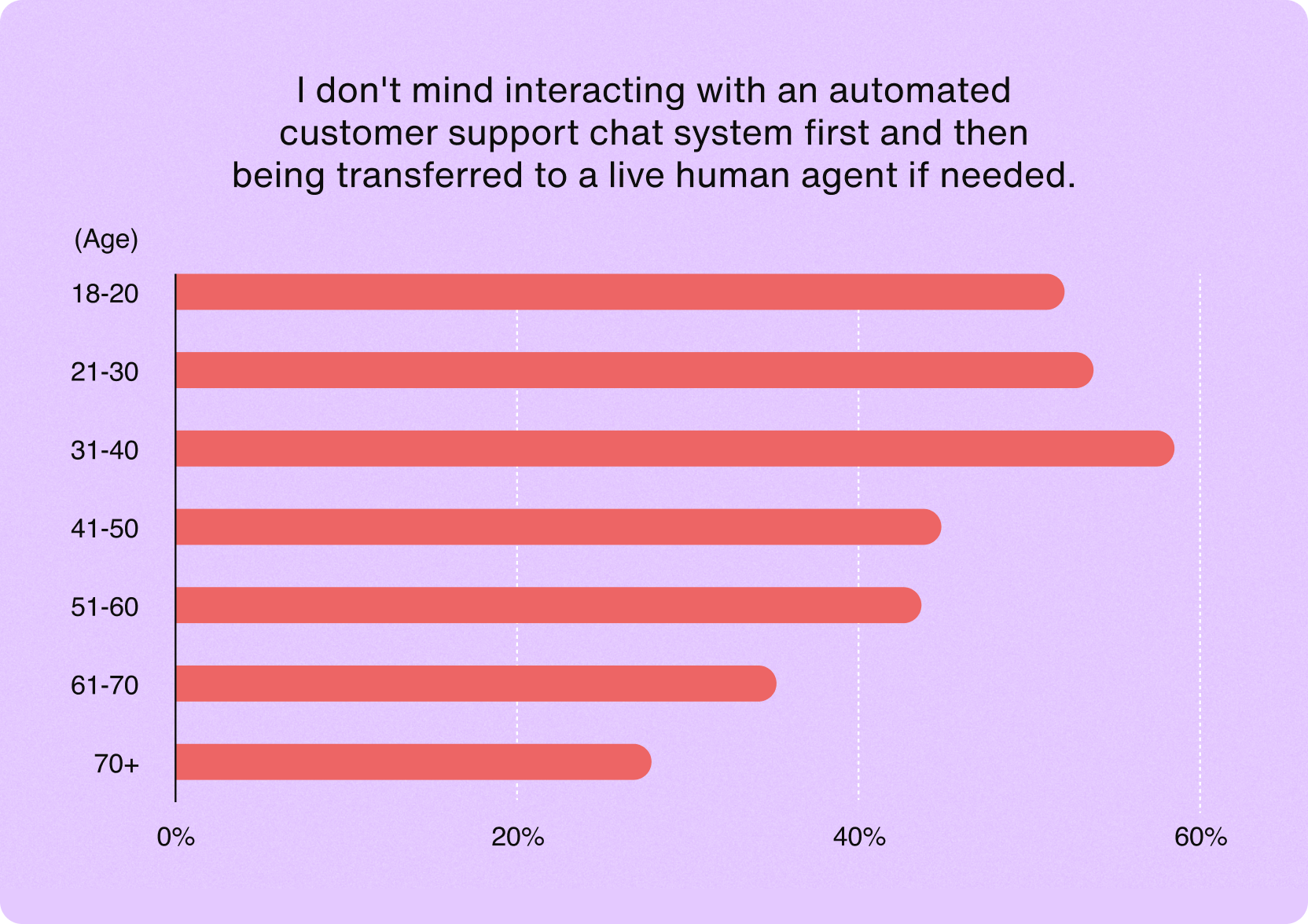
In the same study, results indicated that retention, attention, and advocacy were the results of businesses communicating with consumers using the channels the customers preferred.
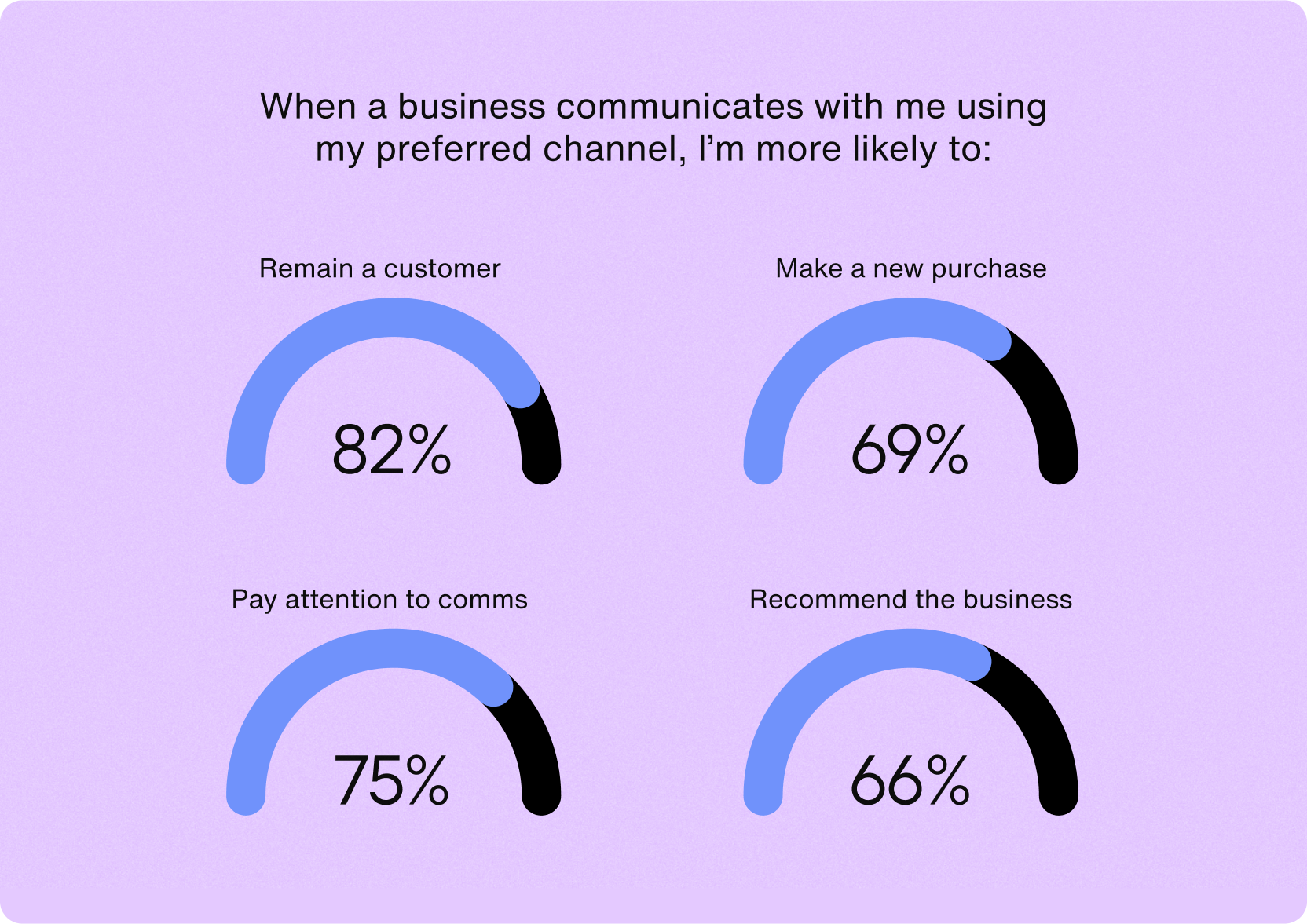
Get the full results of the B2C consumer communication preferences study
It’s clear that consumers are dissatisfied and that the majority wants to interact with chatbots. How can businesses solve for this? With AI chatbots for customer service, of course - but are AI chatbots really as amazing as they’re portrayed? Is their value tangible, or is it a castle in the clouds?
Let’s find out in the next section.
The business perspective on AI in customer service
More than 2 billion people shop online. As the number of online shoppers increases in the years to come, customer service representatives will need to deal with increased support requests. The time, effort, and costs required to resolve customer support issues to the customers’ satisfaction will explode. AI chatbots are a fantastic solution for dealing effectively with this.
Here’s why businesses stand to benefit tremendously from deploying AI chatbots for customer support.
Cost savings
AI chatbots can reduce customer support costs by 30%.
According to Juniper Research, 90% of companies that used chatbots for customer support saw a mere 70¢ cost per interaction and saved 4 minutes per customer support request
The total cost savings due to the implementation of chatbots was $11 billion in 2022.
Productivity savings and efficacy
90% of companies resolve complaints faster with conversational AI solutions.
90% of customer issues are solved in 10 or fewer messages.
AI chatbots can instantly access conversation history, customer preferences, and other relevant data to provide a personalized messaging experience.
Agent productivity
64% of customer support agents who use AI chatbots as part of their work are able to spend more time solving complex customer problems.
Chatbots can handle 80% of routine and repetitive tasks, freeing agents for more strategic work.
42% of B2B customers increase the volume of purchases after a positive customer experience. AI chatbots can facilitate this by acting as an AI assistant to a human support agent.
User preferences
62% of consumers prefer to talk to a chatbot as compared to a human customer service agent.
56% of Gen Z users want more companies to use chatbots. Millennials especially prefer conversing with an AI chatbot instead of a human.
68% of people think that bots can offer fast resolutions to problems.
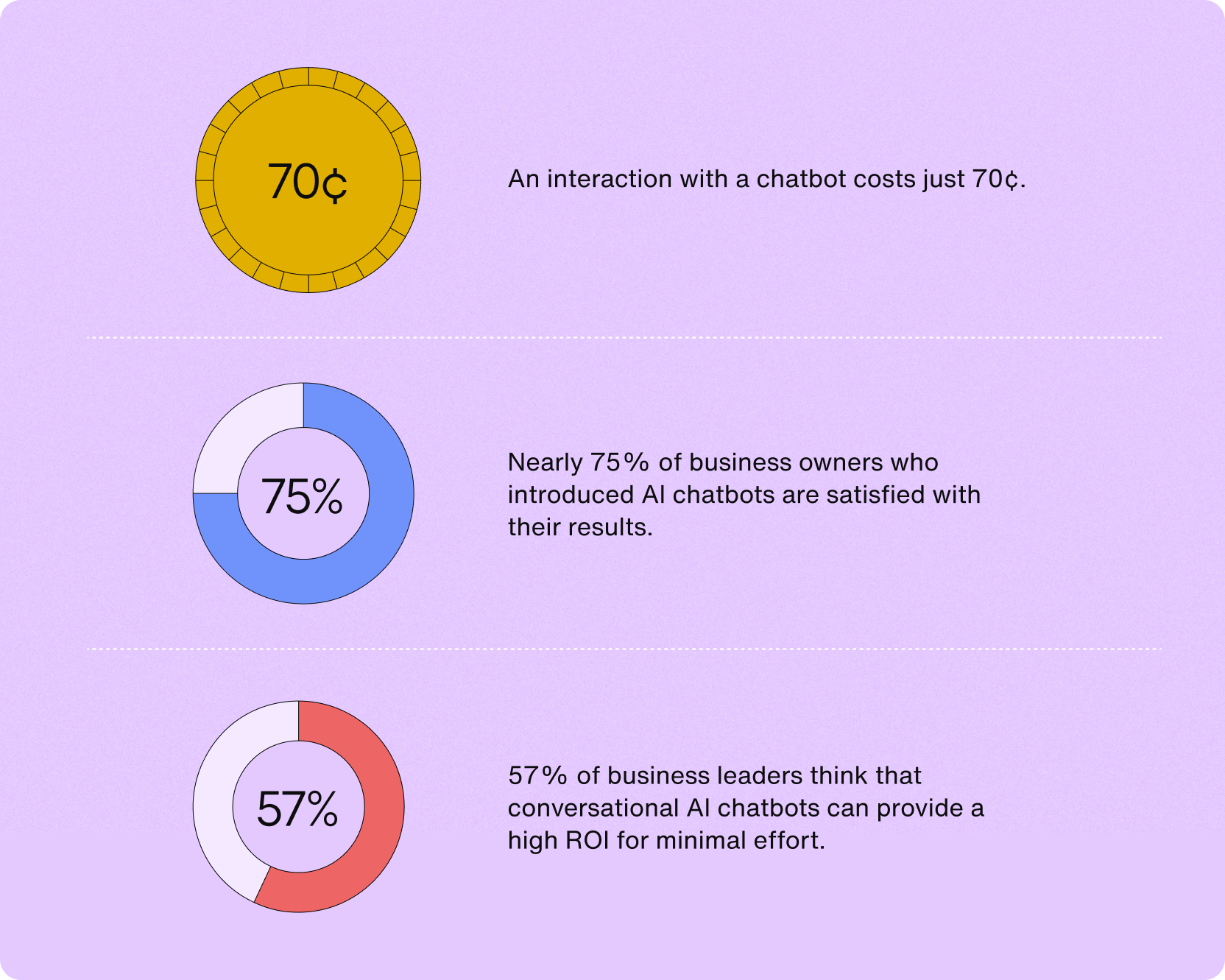
It’s abundantly clear that AI chatbots for customer service deliver better results for both businesses and consumers.
Going beyond the common uses of AI chatbots: Exploring proactive support via generative AI systems and attended AI
Common uses for AI chatbots, such as helping users get quick answers to frequently asked questions, and gathering user feedback, help to save time and money. These uses are rather mainstream today. So, which uses provide a competitive edge to businesses?
Proactive support is a use case at which businesses should take a deeper look.
With the help of generative AI, organizations can leverage the vast amounts of data they access in order to provide hyper-personalized and proactive support to users before they even reach out to customer service. For example, organizations may track the page users are visiting and proactively offer product recommendations or answers to FAQs. This is a great way for businesses to achieve high levels of ticket deflection and resolve queries before they arise.
So, what happens when user queries reach customer service?
A peek at attended AI: The best of humans and bots
If and when user queries do reach customer service, businesses can consider the use of attended AI.
What is attended AI? Attended AI is like a co-pilot or sous chef, attending to routine low-value tasks (such as looking up a customer’s address details or customer ID) in real-time so that agents are freed up to do more strategic work. Using attended AI during customer service conversations enables agents to learn everything they need to know about a customer, even if the data is spread across multiple platforms.
Attended AI can also guide agents through workflows, processes, or tools, as well as coach them in real time to achieve the best business outcome for the conversation. Attended AI, acting as a coach, can speed up agent onboarding and training.
Because attended AI can boost agent productivity and overall levels of well-being (a study by Cornell University found that 88% of call center workers experience high stress!), organizations can achieve a higher ROI.

AI chatbots for customer service: A win-win solution
AI chatbots offer businesses the incentive to save on support costs, agents the opportunity to do more strategic work, and customers to have their issues resolved quickly and with minimal hassle.
It’s clear that AI chatbots have concrete value for all parties involved. Perhaps because of this, the majority of businesses already use or plan to add AI chatbots to their arsenal.
So, how do AI chatbots work? On which technology are AI chatbots based?
Which technology underlies an AI chatbot? An introduction to basic AI concepts
The explosion of worldwide interest in generative AI
ChatGPT’s explosive success has fuelled a worldwide rise in interest in generative AI.
As we can see from Google Trends data, interest in generative AI increased significantly after ChatGPT was released in November 2022.
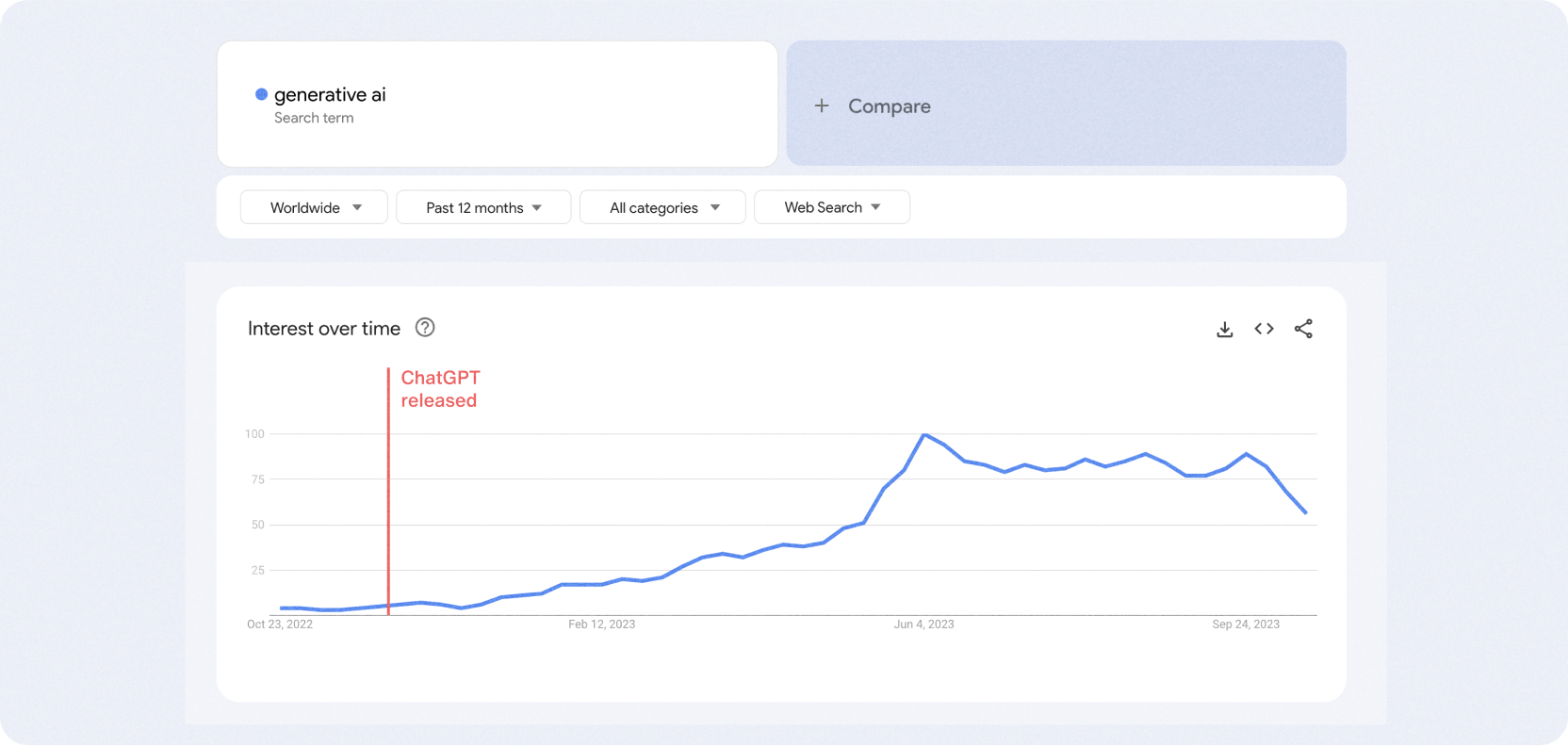
While generative AI is an interesting field that underlies many modern business AI applications, generative AI tends to be a bit of a black box for those not versed in its basic concepts.
Therefore, let’s now demystify some generative AI concepts that you need to know.
Note: This next section discusses technical concepts that underlie generative conversational AI only as it relates to chatbots.
What is generative AI?
Before we go any further, let’s define generative AI.
What is generative AI? According to McKinsey, “Generative artificial intelligence (AI) describes algorithms (such as ChatGPT) that can be used to create new content, including audio, code, images, text, simulations, and videos.”
A generative AI model will create new content that closely resembles examples similar to the data it has ingested. Generative AI models take raw data - which can be anything from a technical user manual to a description of artwork - and create a statistically probable output. Generative AI models are trained on massive datasets; the larger the dataset, the more information the model has to work with while being trained.
When we talk about generative AI, we often use many related terms. What are these terms and what do they mean?
Important AI concepts you need to know before speaking to developers
While you’re likely familiar with some of the terms mentioned here, the below are useful definitions of the important terms. You’ll also see how they overlap.
AI (Artificial Intelligence): An umbrella term that refers to the ability of computers to mimic human intelligence and perform tasks that humans can do to a similar or greater level of accuracy. (Source) AI can sense, reason, and adapt.
ML (Machine Learning): According to AWS, “ML is the science of developing algorithms and statistical models that computer systems use to perform complex tasks without explicit instructions. The systems rely on patterns and inference instead.” (Source) The performance of ML algorithms improves as they are exposed to, and learn from, data over time.
DL (Deep Learning): According to GeeksforGeeks, Deep Learning is a subfield of Machine Learning that involves the use of neural networks to model and solve complex problems. (Source) Neural networks are based on the structure and function of the human brain. Deep learning networks learn from large amounts of data and improve on their own by discovering patterns in data.
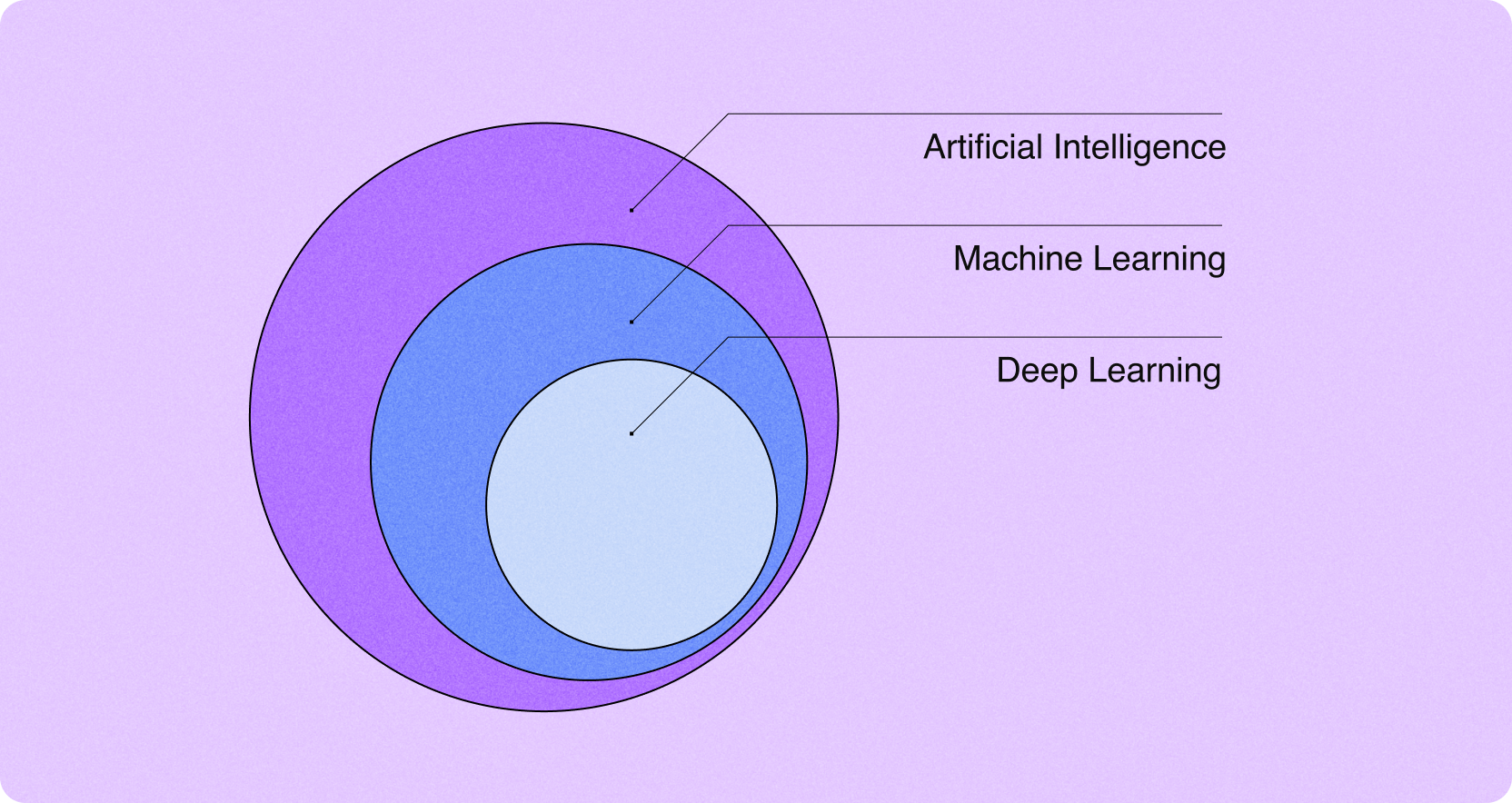
💡 AI vs. ML vs. DL
ML is AI but AI is not necessarily ML!
Similarly, DL is ML but ML is not necessarily DL!
Neural network: According to DeepAI, a neural network is “...a computational learning system that uses a network of functions to understand and translate a data input of one form into a desired output, usually in another form.” Neural networks are modeled on the process by which neurons in the human brain work together to understand sensory input.
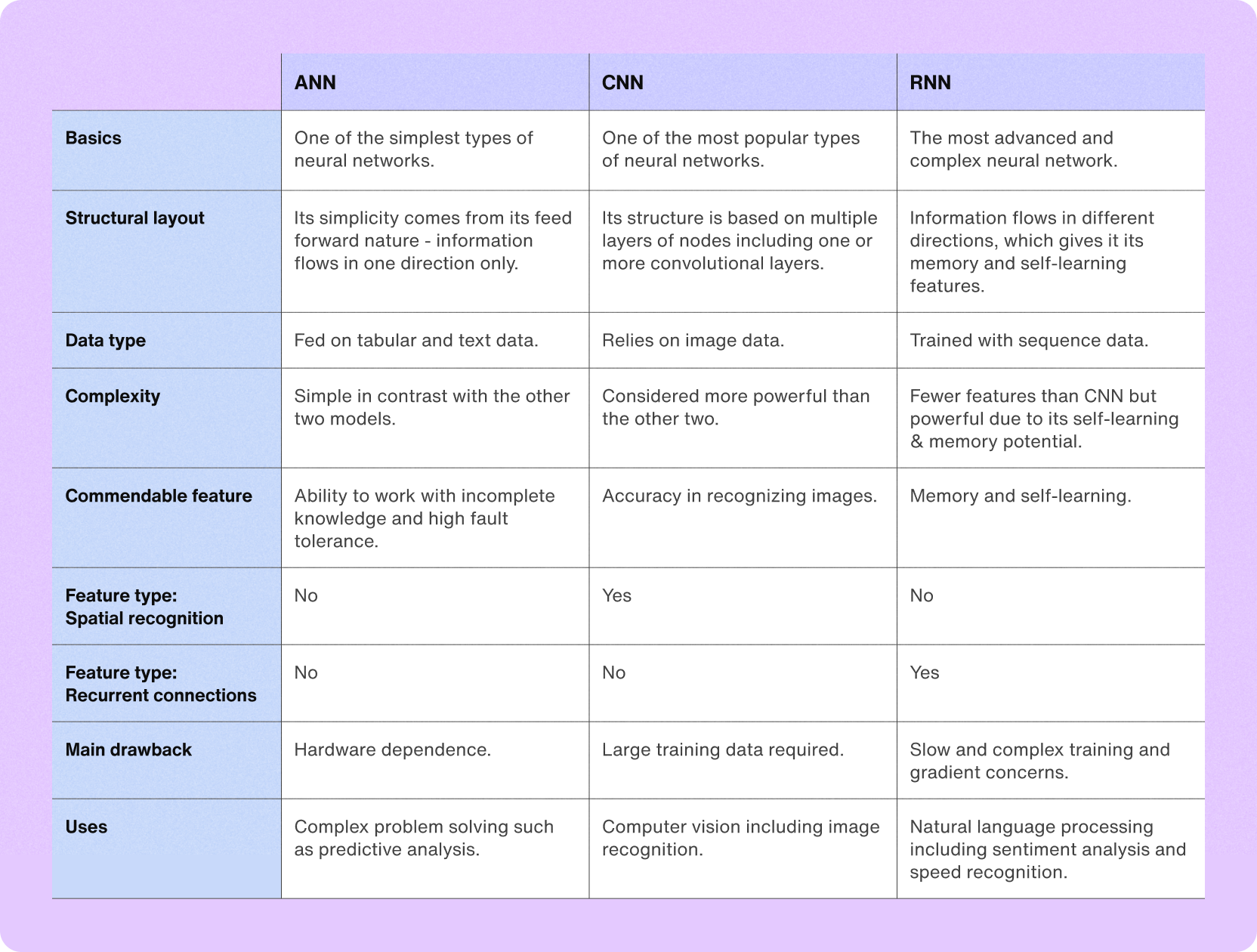
Artificial Neural Network (ANN): A type of neural network “that consists of several processing elements that receive inputs and deliver outputs based on their predefined activation functions.” (Source) An ANN is a feed-forward network (data travels in only one direction) that is useful for pattern recognition, speech-to-text uses, and predictive analysis. (Source)
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN): A type of neural network that is “used primarily for image recognition and processing, due to its ability to recognize patterns in images. A CNN is a powerful tool but requires millions of labeled data points for training.” (Source) A CNN can be used for computer vision and photo tagging suggestions.
Recurrent Neural Network (RNN): An RNN is the most advanced type of neural network. An RNN “RNN works on the principle of saving the output of a particular layer and feeding this back to the input in order to predict the output of the layer.” (Source) They have internal memory, which allows the network to remember things about the input it received, and then use this to make precise predictions about the future. (Source) An RNN is used for applications such as natural language processing and sentiment analysis.
Here’s a useful comparison and more details about the types of neural networks:
ANN vs. CNN vs. RNN
Large Language Models (LLMs): According to Techtarget, “A large language model (LLM) is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm that uses deep learning techniques and massively large data sets to understand, summarize, generate and predict new content.” Put simply, an LLM is has been trained on vast amounts of data in order to be able to generate similar, statistically probable content. A transformer model is a type of LLM and is used to generate human-like content in terms of text, code, and images. (Source)
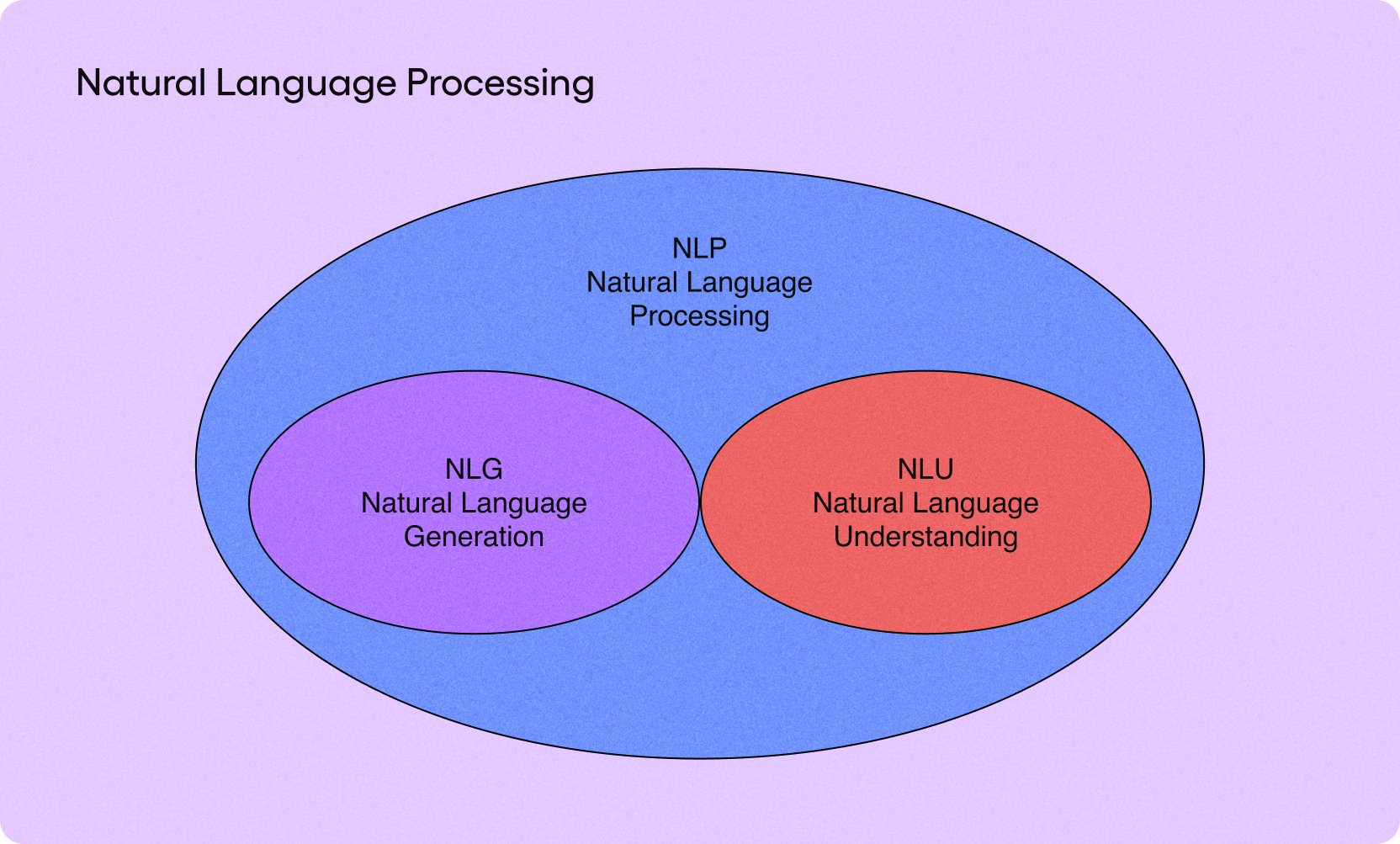
Natural Language Processing (NLP): According to AWS, “Natural language processing (NLP) is a machine learning technology that gives computers the ability to interpret, manipulate, and comprehend human language.” NLP helps to analyze and process text and speech data. It can be used to analyze large documents, call center recordings, and classify or extract text.
Natural Language Understanding (NLU): According to Qualtrics, Natural Language Understanding (NLU) is a field of computer science that analyzes what human language means rather than simply what individual words say. It helps in the analysis of unstructured text, speech, and driving actions such as directing customers to the appropriate service departments.
Natural Language Generation (NLG): According to Qualtrics, “Natural Language Generation, otherwise known as NLG, is a software process driven by artificial intelligence that produces natural written or spoken language from structured and unstructured data.” NLG can be used for many things, from writing summaries of reports to analyzing and generating personalized, humanlike responses to customer support queries.
NLP vs NLU vs NLG
NLP, NLU, and NLG are all related terms. In a nutshell, NLP is an umbrella term that encompasses NLU and NLG.
Supervised learning: According to TechTarget, “Supervised learning is an approach to creating artificial intelligence (AI) where a computer algorithm is trained on input data that has been labeled for a particular output. The model is trained until it can detect the underlying patterns and relationships between the input data and the output labels, enabling it to yield accurate labeling results when presented with never-before-seen data.”
Unsupervised learning: According to TechTarget, “Unsupervised learning is a type of machine learning (ML) technique that uses artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to identify patterns in data sets that are neither classified nor labeled. Unsupervised learning models don't need supervision while training data sets, making it an ideal ML technique for discovering patterns, groupings[,] and differences in unstructured data. It's well-suited for processes such as customer segmentation, exploratory data analysis[,] or image recognition.”
These concepts are certainly useful, but how can you put them to use? It might sound complicated, but it doesn’t have to be! Let’s find out why.
Conversational AI for customer service: See it in action
We’ve seen earlier that a conversational AI chatbot can reduce the time needed to resolve a ticket and lower customer support costs for businesses while providing a faster, more efficient customer experience.
What are some specific ways that an AI chatbot can be used?
Answer FAQs: Provide accurate answers to frequently asked questions so that agents can tackle higher-level questions.
Hold a conversation: Have a basic conversation with a user and resolve low-level queries.
Respond to questions about any URL or file: Set up the bot by feeding it with a URL or file of your choice. The bot will be able to answer questions using this knowledge base.
Transfer to a human agent: Request a human agent to take over if the chatbot cannot answer a question or follow up with an appropriate response.
You can implement all of this with Sendbird’s AI Chatbot.
Here’s an example of what that may look like in Salesforce:

In this video, we can see a ChatGPT-powered AI support chatbot speaking to a user to try to resolve the query before transferring the conversation to an agent.

Build & deploy your own custom AI chatbot in minutes for free
The agent uses Salesforce to manage customer service requests with Sendbird’s Salesforce Connector, which is based on Sendbird’s chat solution and offers a complete chat interface inside the agent’s Salesforce instance.
To get this AI-powered chat functionality within your Salesforce instance, you can use Sendbird’s Salesforce Connector.

Sendbird Chat vs. Salesforce chat: At a glance
Sendbird’s support chat is powerful, and the Salesforce Connector takes it to a whole new level.
Salesforce offers chat as well; here’s why Sendbird’s support chat’s Salesforce Connector is better than the Salesforce Service Cloud chat.
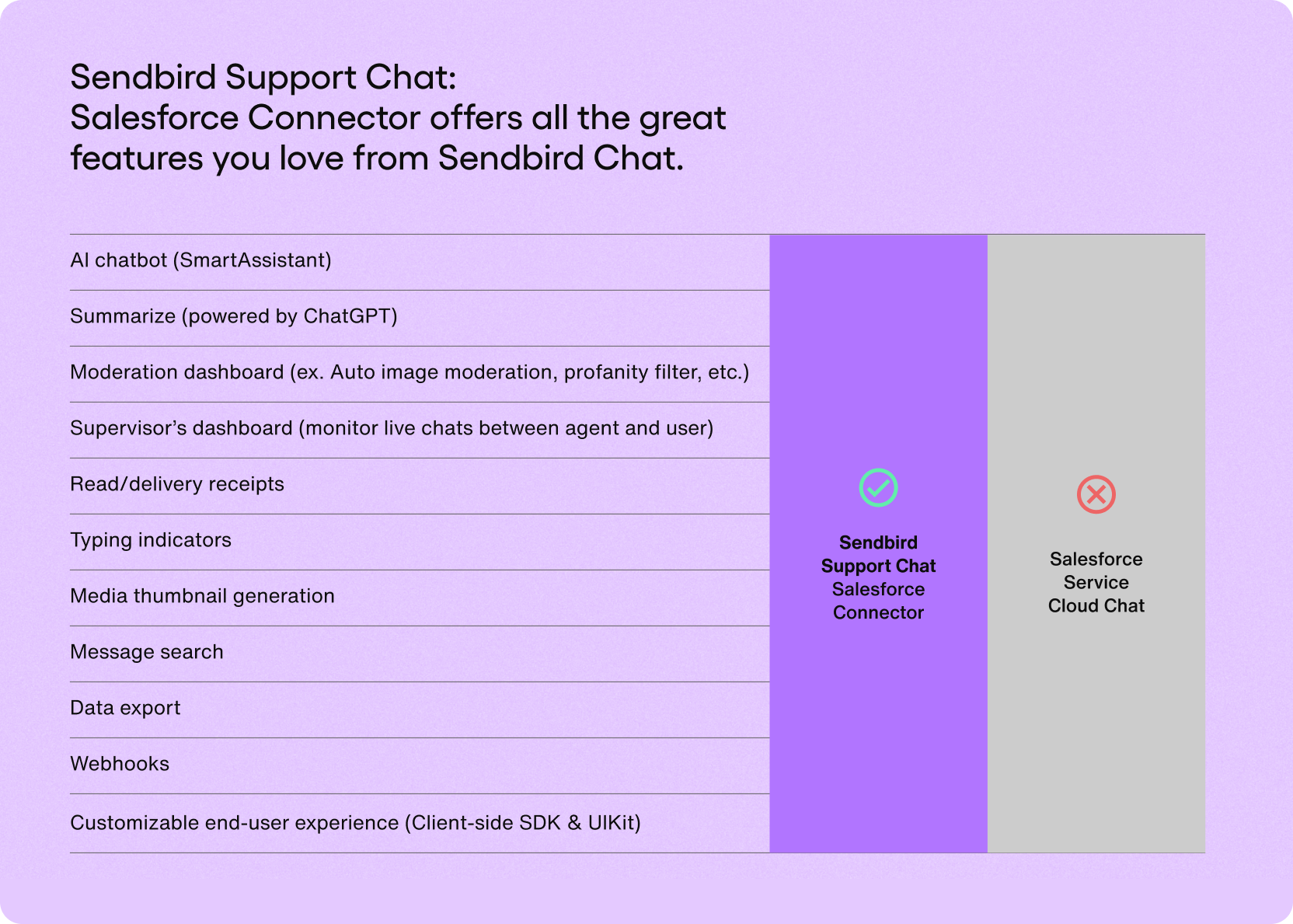
Salesforce Connector: Quick chat summaries powered by ChatGPT
One critically useful attribute of the Salesforce Connector is the Summarize feature. With this, live chat support agents can quickly receive a brief overview, with relevant context, of the customer's issues or concerns without spending unnecessary time rereading the entire chat. The Summarize feature is powered by ChatGPT and takes AI in customer service to the next level.

The video shows us how an agent can use the Salesforce Connector’s Summarize feature to automatically generate accurate, succinct summaries when transferring customer support tickets to a different agent and when closing a case.
Learn more about the Salesforce Connector
How to build an AI chatbot and deploy it on your website or web app
In this section, we will demonstrate how to create a powerful AI chatbot using Sendbird.
Step 1: Sign up for a free Sendbird account
First, create a free Sendbird account. No commitment or credit card is required.
Enter your business email address, choose a strong password, and click Create Account. To manage access properly, use an email address tied to your business.
After you’ve created an account, follow the simple onboarding steps.
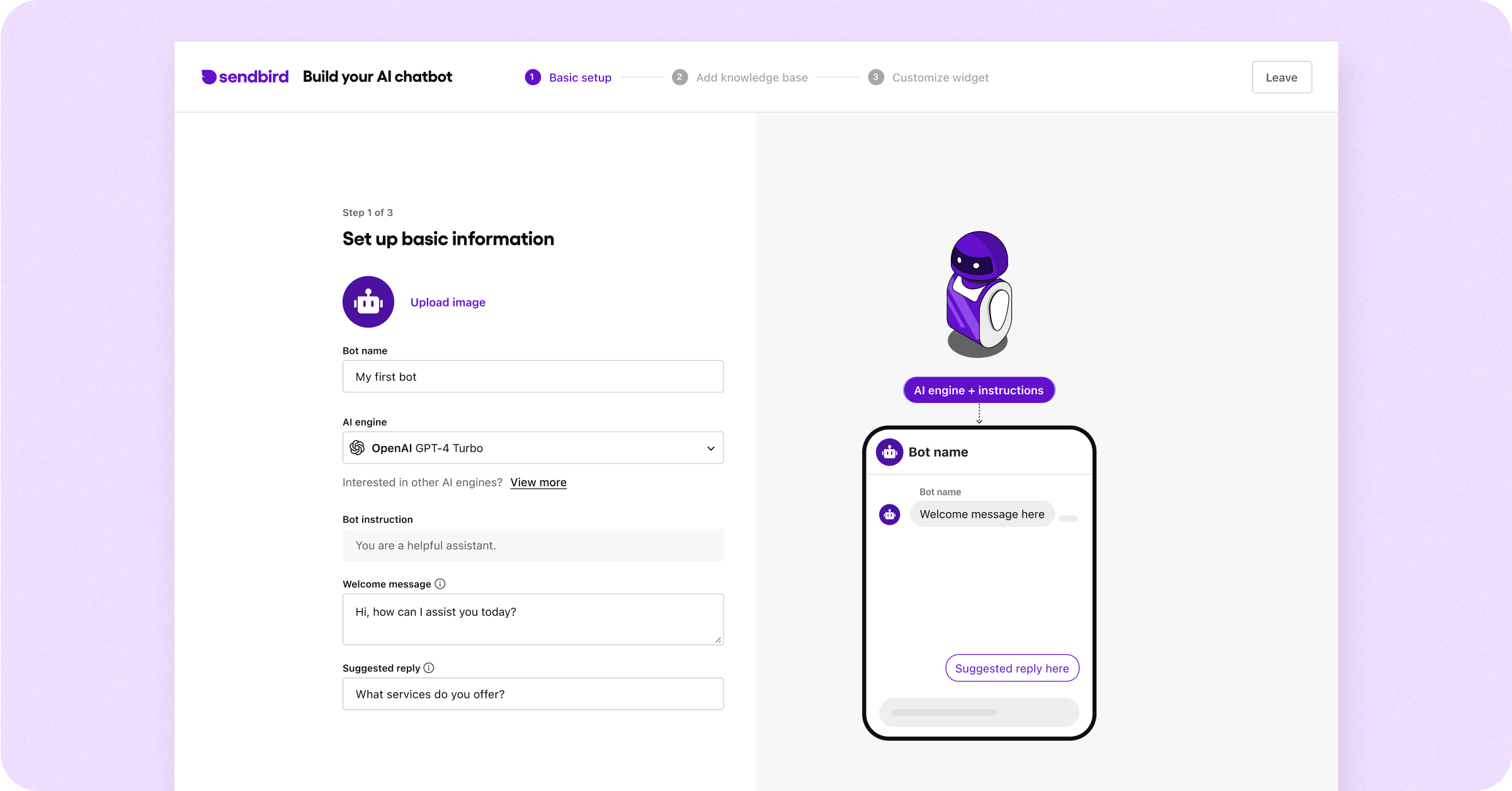
Step 2: Fill out basic information
Provide some essential, basic details about your chatbot. As your needs evolve, you can easily change these settings in the Bot Studio in the Sendbird Dashboard.
For the ‘AI engine’ field, choose OpenAI’s GPT-4o or Anthropic’s Claude 3.5 Sonnet. Consider upgrading to a subscription plan if you prefer a different engine, such as Llama-3 or Solar.
Step 3: Connect a knowledge base to your bot
A chatbot knowledge base is a centralized repository of information that a chatbot uses to provide accurate and relevant responses to user queries. It may contain your proprietary data, FAQs, guidelines, and other resources that the chatbot can reference during interactions. This database enables the chatbot to deliver consistent and reliable information efficiently.
For the purposes of building this sample chatbot, we’ve provided a sample Wikipedia page about the 96th Academy Awards. In this field, we highly recommend that you paste the URL of your own website if you have one. If you don’t have anything to add at the moment, go ahead and add the sample site to test and see how the bot responds with the knowledge base. Scanning the URL can take a few minutes to complete.
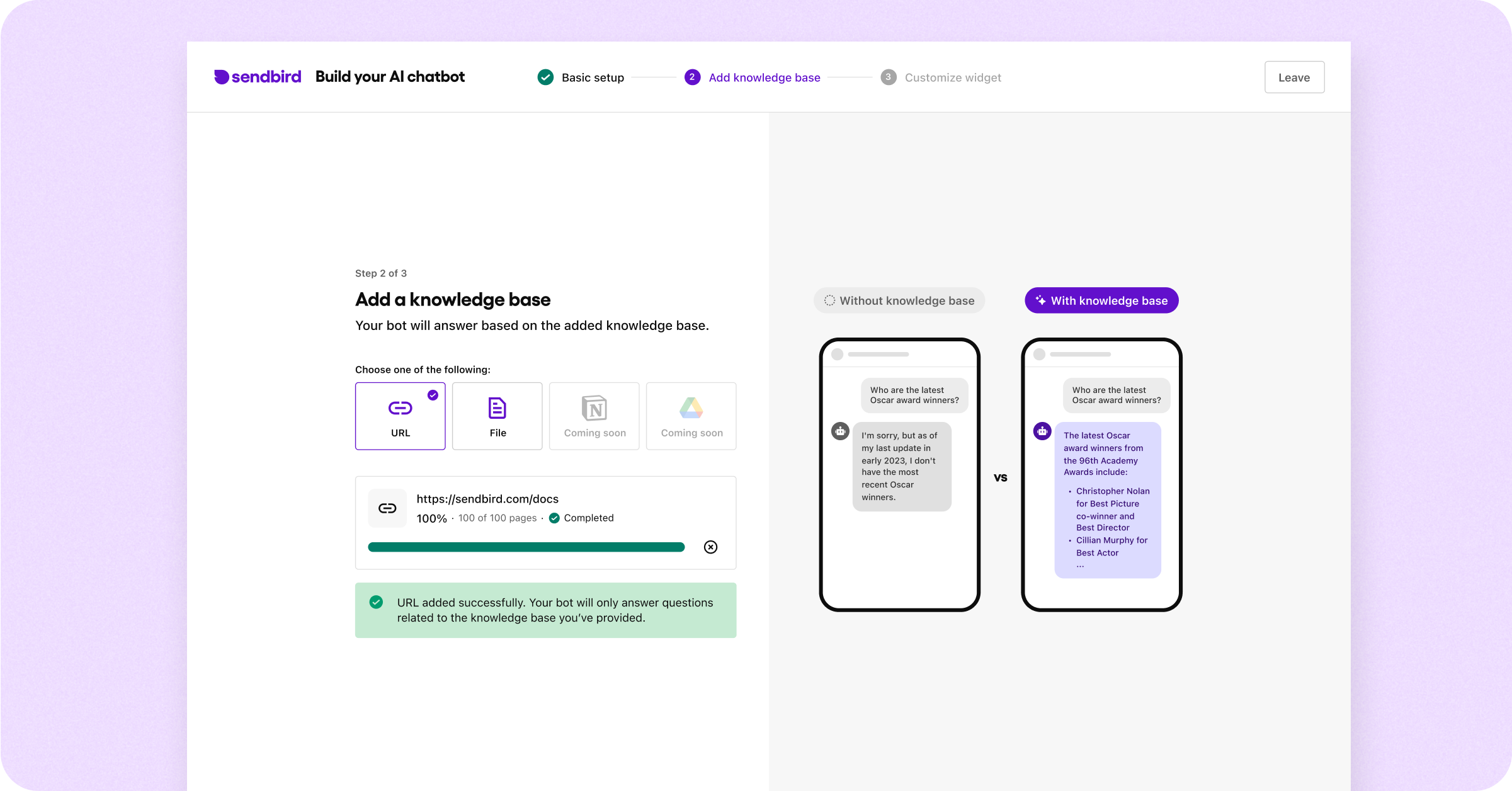
Remember that you can make adjustments to the bot’s knowledge base later!
Step 4: Customize your chatbot’s appearance (Basic chatbot customization)
Sendbird provides chatbot customization options to help you build an AI chatbot that integrates with your customer touchpoints and complements your brand’s online presence. Customize themes, widget colors, and message bubble hues until they align with your company’s brand identity. Changes you make here will update instantly, allowing easy live previewing so you can get your adjustments just right. Remember that you can make adjustments to the bot’s appearance later.
Once you are satisfied with your chatbot’s appearance, click Complete & Preview. This will finalize the chatbot customization for use on your website or app.
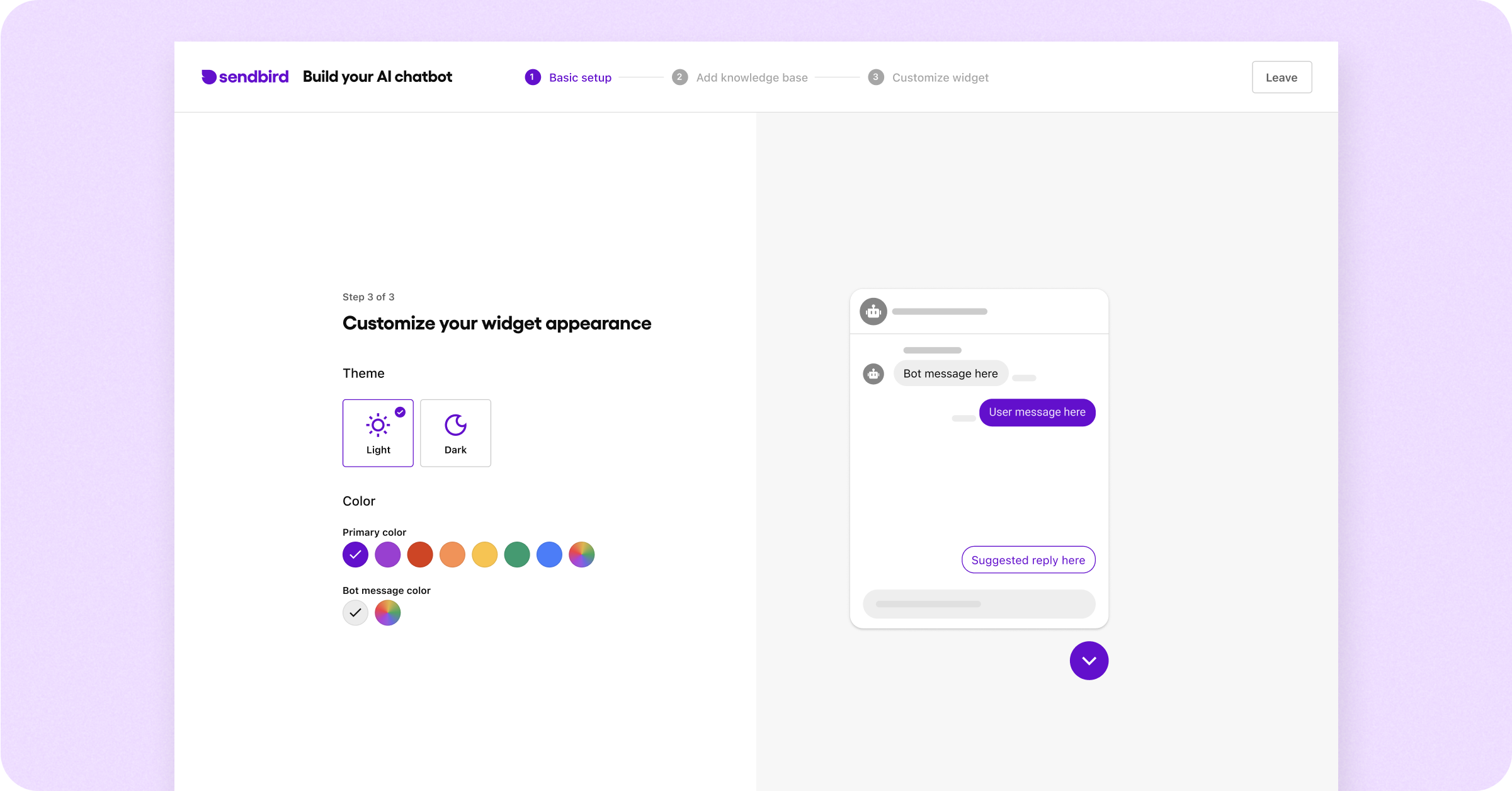
Congratulations, you’ve created your first AI chatbot! 🥳 Now it’s time to test it.
Step 5: Test your AI chatbot
Congratulations on creating your chatbot! Now, it’s time to refine your AI chatbot to help it become truly intelligent. Testing, adjusting, and refining are essential in this phase. You can have a preliminary conversation with your chatbot in the AI chatbot preview (seen below), but we recommend that the bot studio become your testing ground.
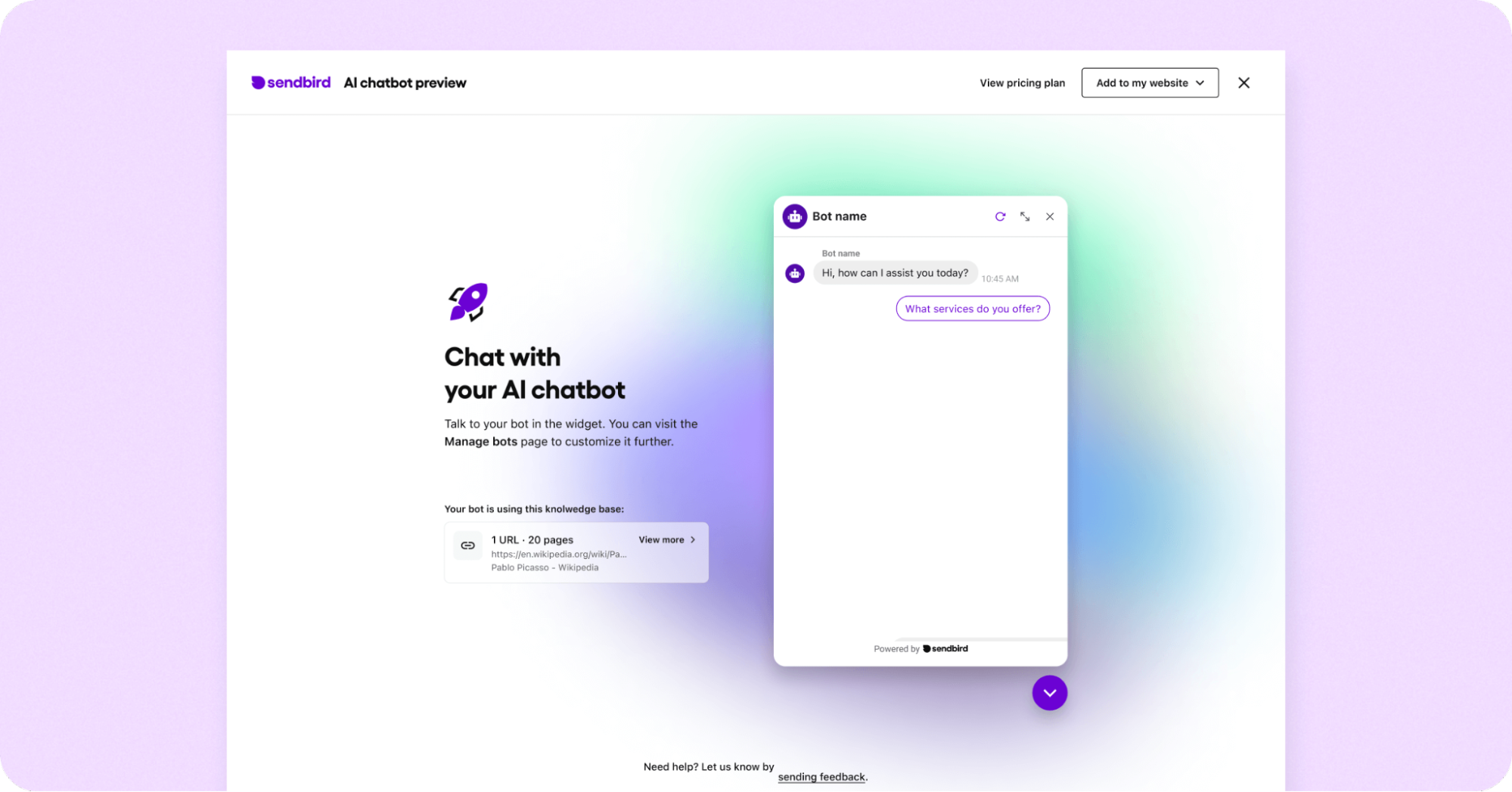
Before we dive into the details, define your testing goals.
Key considerations of chatbot testing
Accurate intent interpretation: LLMs excel at understanding natural language; however, their performance can be further enhanced through some refinement. Define trigger keywords and relevant questions, then test thoroughly to ensure your chatbot handles even the most unexpected edge cases. This can be done by adding trigger keywords directly within the response workflow, by incorporating specific examples into the chatbot’s prompt instructions, or by a combination of these.
Relevant and accurate responses: Your chatbot should always provide valuable, contextually aware answers. Testing will help expose any gaps in its knowledge base or logic.
Graceful fallbacks: No chatbot is perfect. When it can’t interpret a request, the AI chatbot should gracefully transition to a predefined path, such as offering to connect to a human agent, or providing a list of helpful resources. This can be achieved through prompt instructions.
The bot studio provides a good playground for experimentation, which is why we recommend that this becomes your testing ground. In the bot studio, you can test your chatbot against real-world scenarios and immediately see the impact of any changes you make. So, head over to the bot studio (left sidebar in the dashboard -> AI Chatbot -> Bot studio) and select the chatbot you just created:
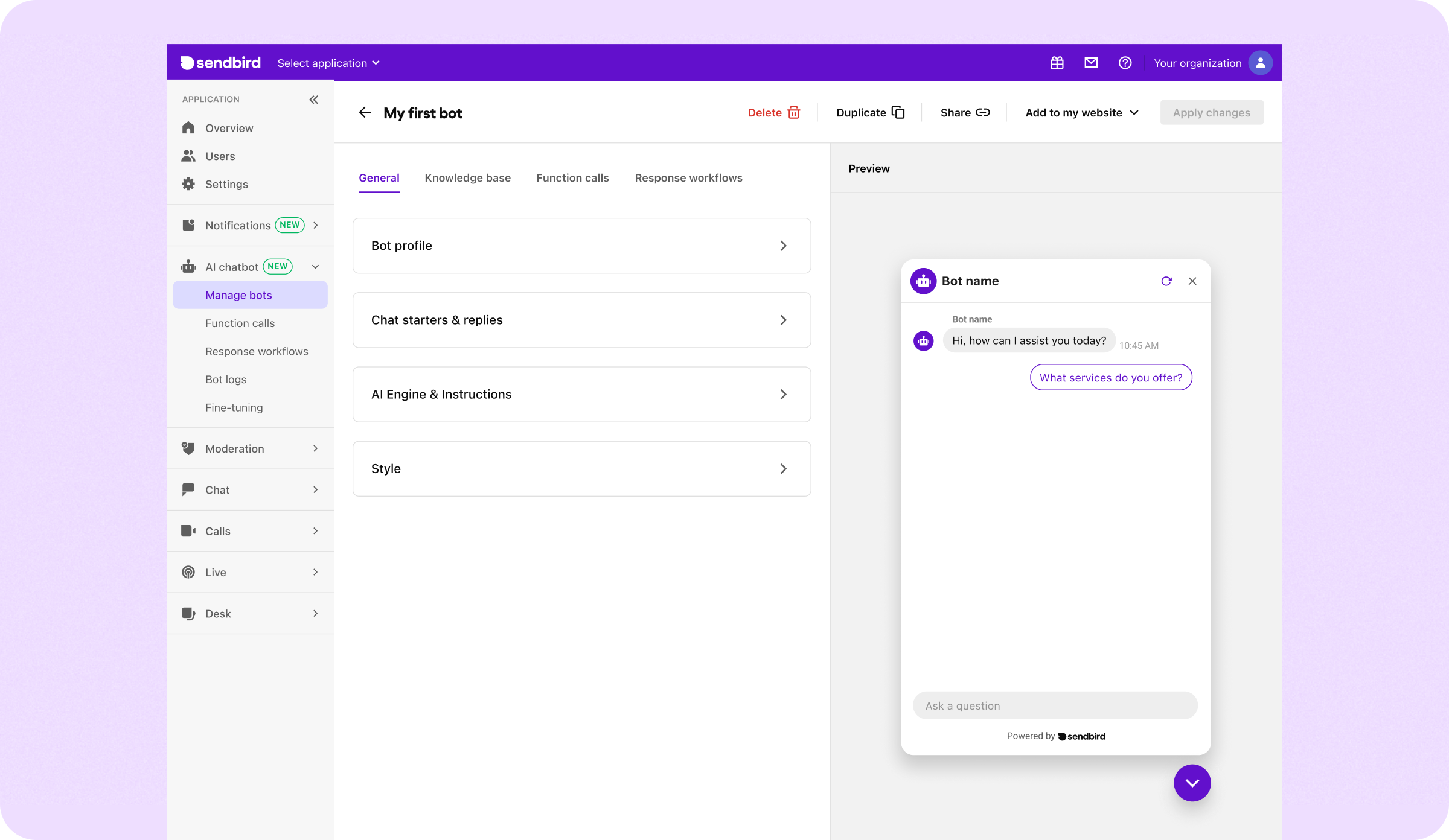
Now start refining your AI chatbot:
- Expand trigger keywords and questions: LLMs work with triggers. Therefore, the more variety you provide, the better the AI chatbot understands what users are asking. Let’s illustrate this with a “coupon offer” flow. If you add trigger keywords or questions such as “discount,” “promo code,” and “Is there a sale going on?”, this will allow AI to detect similar questions to trigger the chatbot to offer a coupon. To start doing this, go to the left sidebar and navigate to AI Chatbot -> Response workflows.
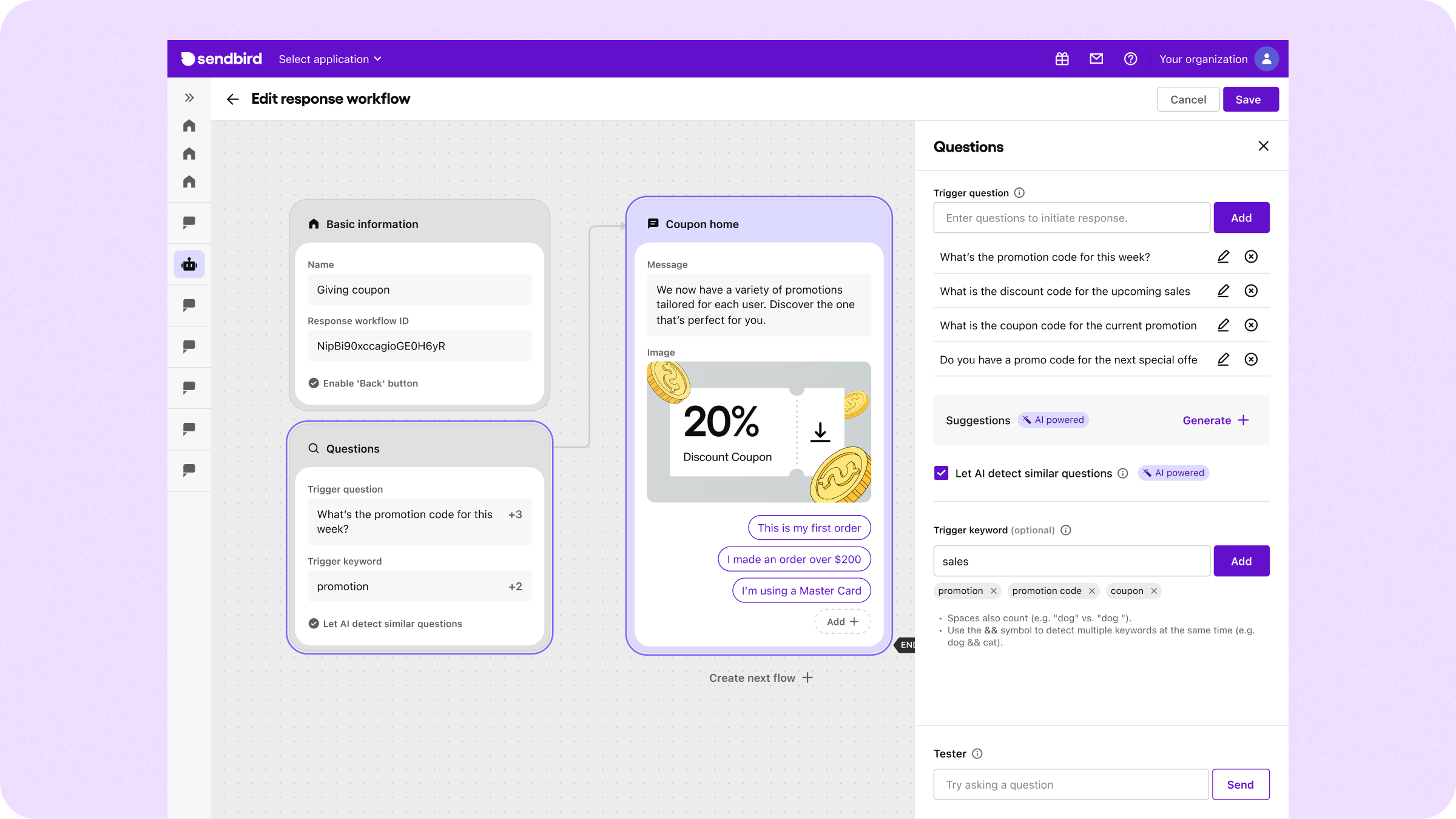
- Enrich your knowledge base: Your chatbot is only as good as the information to which it has access. The more comprehensive and accurate your knowledge base, the more precise and helpful your chatbot’s responses will be. For example, if you’re building a sales bot for your website, upload key documents like your shipping policy, inventory catalogs, and product FAQs.
- Test in bot studio: Now, go back to the bot studio and see if your AI chatbot can accurately identify user intent and deliver relevant responses. You can:
- Simulate conversations: Engage the chatbot in full conversations to see how it handles context and follow-up questions.
- Vary your phrasing: LLMs thrive on variety. The more diverse or varied the triggers, the better the chatbot will grasp user intent.
- Iterate and refine: Remember that testing and refining is an iterative process. The more you test and improve, the more intelligent your chatbot will become!
Step 6: Publish your chatbot widget using AI chatbot integrations
When you’re happy with the chatbot you’ve built, it’s time to publish! The easiest way to publish your AI chatbot is to use our WordPress plugin or Shopify app. These are both simple, no-code integrations to publish your chatbot on your WordPress site or Shopify store.
WordPress users can effortlessly integrate their AI chatbot on their website with a plugin available on the WordPress marketplace and configure it in minutes.
For Shopify users, the easiest way to publish your chatbot widget is to download the Shopify AI chatbot app. Here as well, you can configure the AI chatbot, and get it up and running in minutes.
If you have a working knowledge of websites, consider our Wix, Squarespace, and GoDaddy integration guides. These guides offer a step-by-step process for quickly integrating your AI chatbot and enabling users to start chatting with it!
The video below shows how to deploy the Sendbird AI Chatbot on WordPress, Wix, Squarespace, and to embed the code on your own website.

Build & deploy a custom AI chatbot in minutes for free
Don’t forget the app: In-app customer support powered by conversational AI
In the previous section, you found out how to build an AI chatbot and deploy it on your website or web app. While it’s fantastic to have always-on customer support with an AI chatbot on your website, don’t forget about the tremendous potential of an AI chatbot on your mobile app.
Why is it essential for businesses to have these AI-powered chatbots to handle customer inquiries on the mobile app? First, people use mobile apps almost every time they pick up their phone - indeed, app usage accounts for nearly 90% and almost 4 hours of the time we spend on our phones.
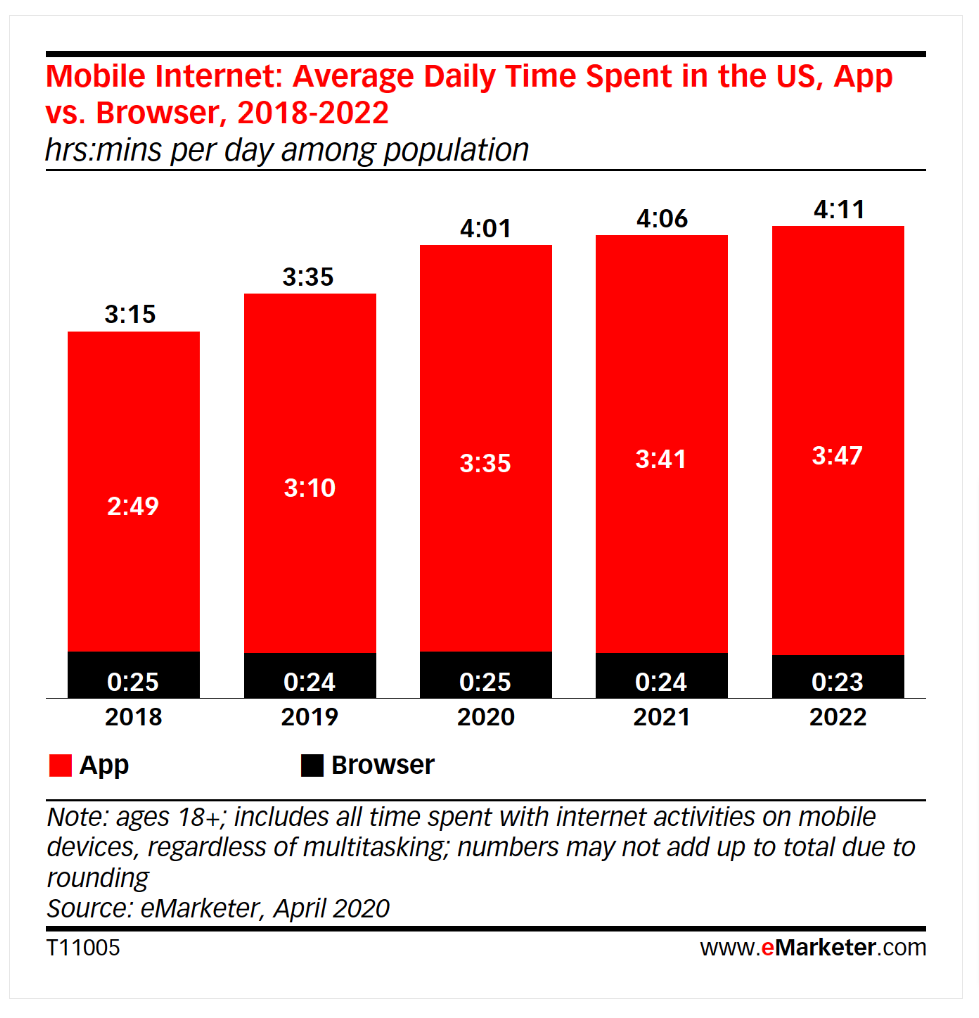
Businesses need to be where their customers are. If customers spend most of their time in apps, then businesses need to communicate with them in the mobile app.
As consumers expect instant responses to their questions, an AI chatbot in the mobile app helps to address this by providing quick answers. Provided internet connectivity is strong, consumers will get instant responses whenever and wherever they are - at home or on the go.
Because businesses meet consumers where they are, this focus on providing AI-powered support through a mobile app can lead to:
Increased customer satisfaction
Better conversion rates
Stronger customer relationships
Far-reaching brand loyalty
Companies can also consider tracking the devices through which customers access chat support and optimizing for mobile as necessary.
As you saw in Chapter 2, Conversational AI has heralded a new reality in chat support. Whether you decide to use this for chat support in your mobile app or on your website, you will likely see the same fantastic benefits.
What is the impact of conversational AI in customer support?
Sendbird’s conversational AI solution for customer support allows customer service agents to:
Reduce time to ticket resolution by 30%
Increase agent productivity by 30% - 50%
Increase CSAT by 2%
Revisit customer support AI in action
Here’s how Sendbird’s conversational AI solution for customer support helped our customers.
Super Home: Subscription-based home care services for homeowners
"Sendbird was the perfect solution to fulfilling our goal of enabling direct communication between subscribers and service providers through chat. With Sendbird’s customizable chat API, we could use - and pay for - only the features we needed. Sendbird’s chat solution also offered tremendous flexibility for us to implement our own bots in the future. And best of all, it was 50% cheaper than other solutions!"
Marijana Vlahović, Senior Product Manager at Super Home
Traveloka: Southeast Asia’s leading travel platform operating in 6 markets across Southeast Asia
- Key result: Today, more than 55 million monthly active users enjoy integrated customer services and no longer face the challenge of disconnected support chats.
"The chat that we built upon Sendbird is the number one communication channel among all of the communication channels that we use or that we provide to all our users. Sendbird provides the best solution in terms of the technical capability and the amount of information that the Sendbird team could provide us, as well as [their] professionalism."
Adi Alimin, Senior Product Manager at Traveloka

Putting it all together: Start building an AI-powered customer support solution on Sendbird’s conversations platform
Whether you’re looking to supercharge an already robust customer service arm of your company, or you want to streamline the work of a lean customer service team, building an AI-powered customer support solution will yield results for your business. Agents will receive the support they need, CSAT will increase, and your business’s revenue will grow.
When you’re ready to implement an AI customer service solution, our experts are ready to walk you through the first steps. We look forward to assisting you in any way possible with your project!
If you’re ready to transform your customer interactions, start a free trial of Sendbird’s AI Chatbot, Desk, or Salesforce Connector today and experience the difference that advanced technology can make in enhancing both customer support and customer service.

Build & deploy your own custom AI chatbot in minutes for free













